BCAAとEAA ~BCAAの効果~
掲載日:2019.02.01

退屈な話が続きましたが、いよいよアミノ酸それぞれの解説をしていくことにしましょう。まずはBCAAからです。
BCAAとはなにか
これは「バリン」と「ロイシン」、「イソロイシン」の3つのアミノ酸を指します。これらのアミノ酸は側鎖が全て枝分かれ(BranchedChain)した構造を持っていますので、"Branched Chain Amino Acids"の頭文字をとって、BCAAと呼ぶことになっています。
芳香族アミノ酸(チロシンやフェニルアラニン、トリプトファン)が肝臓で代謝されるのに対し、BCAAは主に筋肉で代謝されます。
なお筋タンパクの16%がBCAAを構成成分としており、これは1kgの筋肉あたり約32gとなります。(※88)
アミノ酸プールにもBCAAは存在していますが、かなりの低濃度であり(約650uM)、筋肉1kgあたり0.1gにもなりません。また血中のBCAA濃度も約400uM程度に過ぎません。
しかしサプリメントとしてBCAAを摂取すると、30分程度で血中濃度はピークに達します。5gのBCAAを摂取することで、通常の320%もの血中濃度になり、2時間後には元のレベルに戻ります。(※89)
この急激な濃度変化により、BCAAは様々な生理作用を示すと考えられています。
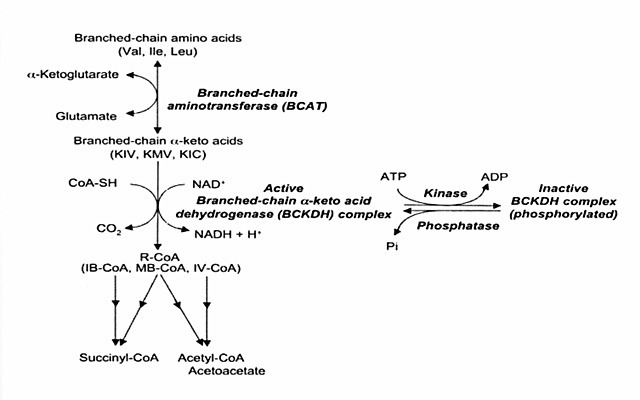
摂取したBCAAは分岐鎖アミノ酸アミノ基転移酵素(BCAT)によって分岐鎖αケト酸になります。そして分岐鎖αケト酸は分岐鎖αケト酸脱水素酵素複合体(BCKDC)によってCoA化合物となり、それがアセチルCoAやアセト酢酸、スクシニルCoAになります。(※90)
BCAAの代謝について、こちらに載せておきましょう。
芳香族アミノ酸(チロシンやフェニルアラニン、トリプトファン)が肝臓で代謝されるのに対し、BCAAは主に筋肉で代謝されます。
なお筋タンパクの16%がBCAAを構成成分としており、これは1kgの筋肉あたり約32gとなります。(※88)
アミノ酸プールにもBCAAは存在していますが、かなりの低濃度であり(約650uM)、筋肉1kgあたり0.1gにもなりません。また血中のBCAA濃度も約400uM程度に過ぎません。
しかしサプリメントとしてBCAAを摂取すると、30分程度で血中濃度はピークに達します。5gのBCAAを摂取することで、通常の320%もの血中濃度になり、2時間後には元のレベルに戻ります。(※89)
この急激な濃度変化により、BCAAは様々な生理作用を示すと考えられています。
摂取したBCAAは分岐鎖アミノ酸アミノ基転移酵素(BCAT)によって分岐鎖αケト酸になります。そして分岐鎖αケト酸は分岐鎖αケト酸脱水素酵素複合体(BCKDC)によってCoA化合物となり、それがアセチルCoAやアセト酢酸、スクシニルCoAになります。(※90)
BCAAの代謝について、こちらに載せておきましょう。
BCAAの効果
さて、BCAAにはどのような効果があるのでしょうか。箇条書きで説明していきます。
1.筋肉を増やす
前述しましたが、タンパク合成を活性化するmTORシグナル伝達経路をBCAA(特にロイシン)が活性化します。(※91)
またロイシンはインスリン分泌も刺激して、こちらの方向からもタンパク合成を高めます。(※92)さらにミオスタチンを減らすことにより筋肉を増やすという効果も認められています。(※93)
またロイシンはリソソーム系におけるオートファゴソーム形成の阻害や、タンパク分解酵素であるプロテアソームを阻害してタンパク分解を防ぐ作用もあり(※94、※95)、特に低栄養児における筋肉の減少を防ぐ効果が知られています。
12名の男子大学生を対象にBCAAを一日12g摂取させてハードな水泳を行わせた実験では、筋分解の指標である尿素窒素やトリメチルヒスチジン、ヒドロキシプロリンのレベルが顕著に低下していました。(96)
つまりBCAAはタンパク合成を高め、同時にタンパク分解を減少させることによって筋肉を増やしてくれるのです。
またロイシンはインスリン分泌も刺激して、こちらの方向からもタンパク合成を高めます。(※92)さらにミオスタチンを減らすことにより筋肉を増やすという効果も認められています。(※93)
またロイシンはリソソーム系におけるオートファゴソーム形成の阻害や、タンパク分解酵素であるプロテアソームを阻害してタンパク分解を防ぐ作用もあり(※94、※95)、特に低栄養児における筋肉の減少を防ぐ効果が知られています。
12名の男子大学生を対象にBCAAを一日12g摂取させてハードな水泳を行わせた実験では、筋分解の指標である尿素窒素やトリメチルヒスチジン、ヒドロキシプロリンのレベルが顕著に低下していました。(96)
つまりBCAAはタンパク合成を高め、同時にタンパク分解を減少させることによって筋肉を増やしてくれるのです。
2.持久力を増やす
炭水化物とBCAA、カフェインを配合したドリンクを飲んで2時間のランニングを行った実験において、通常よりも高いパフォーマンスを発揮することができたという報告があります。(※97)
また70%VO2maxでサイクリングを行った研究ではBCAA摂取によって運動後の筋ダメージを明らかに抑えることができています。(※98)
特にグリコーゲンが枯渇した状態では、BCAAが脂肪酸の酸化によるエネルギー合成を高めるため、疲労が起こりにくくなるようです。(※99)
また70%VO2maxでサイクリングを行った研究ではBCAA摂取によって運動後の筋ダメージを明らかに抑えることができています。(※98)
特にグリコーゲンが枯渇した状態では、BCAAが脂肪酸の酸化によるエネルギー合成を高めるため、疲労が起こりにくくなるようです。(※99)
3.体脂肪を減らす
BCAAはダイエットにも役立ちます。40歳から59歳の男女4429名を対象にした調査では、BCAA摂取量が多いと過体重や肥満になりにくいことが示されています。(※100)
また25名のエリートレスラーがダイエットと並行してBCAAを摂取したところ、特に腹部の脂肪を減らすことができたという報告があります。(※101)
高脂肪食マウスの実験ですが、ロイシン摂取量を2倍にしたところ、体重の増加が32%抑制され、褐色および白色脂肪組織、そして筋肉におけるUCP-3の増加に伴う安静時基礎代謝が増加しました。
またインスリン感受性が高まり、グルカゴンや糖新生アミノ酸が減少、さらにLDLコレステロールも低下(27~53%)しています。(※102)
さらにロイシンはmTORを活性化することにより筋タンパクを合成するだけでなく、体内にエネルギーが増加していると感じさせることにより、食欲を減らすことができます。
それだけでなく、満腹ホルモンであるレプチン感受性を高めてレプチンの働きを高めたり、食後のレプチン上昇を調整したりすることにより、食欲を抑える作用があるようです(※103,※104)
また25名のエリートレスラーがダイエットと並行してBCAAを摂取したところ、特に腹部の脂肪を減らすことができたという報告があります。(※101)
高脂肪食マウスの実験ですが、ロイシン摂取量を2倍にしたところ、体重の増加が32%抑制され、褐色および白色脂肪組織、そして筋肉におけるUCP-3の増加に伴う安静時基礎代謝が増加しました。
またインスリン感受性が高まり、グルカゴンや糖新生アミノ酸が減少、さらにLDLコレステロールも低下(27~53%)しています。(※102)
さらにロイシンはmTORを活性化することにより筋タンパクを合成するだけでなく、体内にエネルギーが増加していると感じさせることにより、食欲を減らすことができます。
それだけでなく、満腹ホルモンであるレプチン感受性を高めてレプチンの働きを高めたり、食後のレプチン上昇を調整したりすることにより、食欲を抑える作用があるようです(※103,※104)
4.回復を促進する
BCAAは筋ダメージを急速に回復することにより、トレーニングによる筋肉痛を軽減することができます。(※105、※106、※107)
またBCAAはインスリンの働きを強化することができます。ブドウ糖にホエイプロテインを追加して摂取することにより、エクササイズ後のグリコーゲン回復を促進させることができています。(※108、※109)
またBCAAはインスリンの働きを強化することができます。ブドウ糖にホエイプロテインを追加して摂取することにより、エクササイズ後のグリコーゲン回復を促進させることができています。(※108、※109)
5.集中力をアップさせる
血液中にはアルブミンというタンパク質が存在します。
そして普段はアルブミンにアミノ酸のトリプトファンが結合しています。
しかし運動時など、脂肪がエネルギーとして動員されるときは脂肪酸がアルブミンと結合しようとします。するとアルブミンはトリプトファンを離してしまいます。そしてトリプトファンはフリーとなるため、脳に入ることができるようになります。(※110)
脳に入ったトリプトファンはセロトニンとなり、これが精神的な疲労の原因になるという説があります。実際、セロトニン受容体の活性化は筋収縮の発火頻度を低下させるという報告があります。(※111)
BCAAも脳に入ることができるのですが、このときにトリプトファンと同じ運搬体を使います。つまりBCAAを摂取することにより、トリプトファンが脳に入るのを防ぐことができるわけです。そのため、BCAAの摂取は脳内セロトニンを減らし、精神的な疲労を軽減すると言われています。(※112)
なお12名の男性テコンドー選手を対象にした研究や、22名の男女ハンドボール選手を対象にした研究で、BCAAとアルギニンを同時に摂収したところ、非摂取群と比較して顕著にスプリントパフォーマンスの改善や、中枢性疲労が軽減されたという報告もあります。(※113,※114)
88 : Nutraceutical Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Skeletal Muscle J Nutr. 2006;136(2):5298–532S.
89 : Effects of branched-chain amino acid supplementation on plasma concentrations of free amino acids, insulin, and energy substrates in young men. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2011;57(1):114-7.]
90 : Branched-chain amino acid catabolism in exercise and liver disease. J Nutr. 2006 Jan;136(1 Suppl):250S-3S.
91 : Role of leucine in the regulation of mTOR by amino acids: revelations from structure-activity studies. J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3):8615-865S.
92:Leucine promotes glucose uptake in skeletal muscles of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Dec 20;299(5):693-6
93: L-leucine, beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid (HMB) and creatine monohydrate prevent myostatin-induced Akirin-1/Mighty mRNA down-regulation and myotube atrophy. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2014 Aug 13;11:38. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-11-38. eCollection 2014.
94 : Nutrient control of macroautophagy in mammalian cells. Mol Aspects Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;27(5-6):426-43. Epub 2006 Sep 26.
95 : Branched-chain amino acids and arginine suppress MaFbx/atrogin-1 mRNA expression via mTOR pathway in C2C12 cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1780(10):1115-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Jun 18.
96 : Influence of branched-chain amino acid supplementation on urinary protein metabolite concentrations after swimming. J Am Coll Nutr. 2006 Jun;25(3):188-94.
97 : Effects of carbohydrates-BCAAs-caffeine ingestion on performance and neuromuscular function during a 2-h treadmill run: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over placebo-controlled study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011 Dec 7;8:22. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-22.
98 : Effect of BCAA intake during endurance exercises on fatigue substances, muscle damage substances, and energy metabolism substances. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2013 Dec;17(4):169-80. doi: 10.5717/jenb.2013.17.4.169. Epub 2013 Nov 28.
99 : Branched-chain amino acids supplementation enhances exercise capacity and lipid oxidation during endurance exercise after muscle glycogen depletion. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011 Mar;51(1):82-8.
100 : Higher branched-chain amino acid intake is associated with a lower prevalence of being overweight or obese in middle-aged East Asian and Western adults. J Nutr. 2011 Feb;141(2):249-54. doi: 10.3945/jn. 110.128520. Epub 2010 Dec 15.
101 : Combined effects of caloric restriction and branched-chain amino acid supplementation on body composition and exercise performance in elite wrestlers. Int J Sports Med. 1997 Jan;18(1):47-55.
102 : Increasing Dietary Leucine Intake Reduces Diet-Induced Obesity and Improves Glucose and Cholesterol Metabolism in Mice via
103 : Leucine in food mediates some of the postprandial rise in plasma leptin concentrations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Sep;291(3):E621-30. Epub 2006 Apr 25.
104 : Leucine supplementation improves leptin sensitivity in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Nutr Res. 2015 Jun 25;59:27373. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v59.27373. eCollection 2015.
105 : Branched-chain amino acid ingestion can ameliorate soreness from eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 May;42(5):962-70. doi: 10.1249/MSS.Ob013e3181c1b798.
106 : Branched-chain amino acid supplementation before squat exercise and delayed-onset muscle soreness. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2010 Jun;20(3):236-44.
107 : Exercise-induced muscle damage is reduced in resistance-trained males by branched chain amino acids: a randomized, double-blind,
108 : Post-exercise carbohydrate plus whey protein hydrolysates supplementation increases skeletal muscle glycogen level in rats. Amino Acids. 2010 Apr;38(4):1109-15. 10.1007/s00726-009-0321-0. Epub 2009 Jul 11.
doi:
109 : Branched-chain amino acid-containing dipeptides, identified from whey protein hydrolysates, stimulate glucose uptake rate in L6 myotubes and isolated skeletal muscles. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2009 Feb;55(1):81-6.
110 : Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. 1971. Obes Res. 1997 Jul;5(4):377-80.
111 : Serotonin spillover onto the axon initial segment of motoneurons induces central fatigue by inhibiting action potential initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2013 Mar 19;110(12):4774-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216150110. Epub 2013 Mar 4.
112 : A role for branched-chain amino acids in reducing central fatigue. J Nutr. 2006 Feb;136(2):544S-547S.
113: Branched-chain amino acids, arginine, citrulline alleviate central fatigue after 3 simulated matches in taekwondo athletes: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016 Jul 13;13:28. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0140-0. eCollection 2016.
114 : Branched-chain amino acids and arginine improve performance in two consecutive days of simulated handball games in male and female athletes: a randomized trial. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 24;10(3):e0121866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121866. eCollection 2015.
そして普段はアルブミンにアミノ酸のトリプトファンが結合しています。
しかし運動時など、脂肪がエネルギーとして動員されるときは脂肪酸がアルブミンと結合しようとします。するとアルブミンはトリプトファンを離してしまいます。そしてトリプトファンはフリーとなるため、脳に入ることができるようになります。(※110)
脳に入ったトリプトファンはセロトニンとなり、これが精神的な疲労の原因になるという説があります。実際、セロトニン受容体の活性化は筋収縮の発火頻度を低下させるという報告があります。(※111)
BCAAも脳に入ることができるのですが、このときにトリプトファンと同じ運搬体を使います。つまりBCAAを摂取することにより、トリプトファンが脳に入るのを防ぐことができるわけです。そのため、BCAAの摂取は脳内セロトニンを減らし、精神的な疲労を軽減すると言われています。(※112)
なお12名の男性テコンドー選手を対象にした研究や、22名の男女ハンドボール選手を対象にした研究で、BCAAとアルギニンを同時に摂収したところ、非摂取群と比較して顕著にスプリントパフォーマンスの改善や、中枢性疲労が軽減されたという報告もあります。(※113,※114)
88 : Nutraceutical Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Skeletal Muscle J Nutr. 2006;136(2):5298–532S.
89 : Effects of branched-chain amino acid supplementation on plasma concentrations of free amino acids, insulin, and energy substrates in young men. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2011;57(1):114-7.]
90 : Branched-chain amino acid catabolism in exercise and liver disease. J Nutr. 2006 Jan;136(1 Suppl):250S-3S.
91 : Role of leucine in the regulation of mTOR by amino acids: revelations from structure-activity studies. J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3):8615-865S.
92:Leucine promotes glucose uptake in skeletal muscles of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Dec 20;299(5):693-6
93: L-leucine, beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid (HMB) and creatine monohydrate prevent myostatin-induced Akirin-1/Mighty mRNA down-regulation and myotube atrophy. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2014 Aug 13;11:38. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-11-38. eCollection 2014.
94 : Nutrient control of macroautophagy in mammalian cells. Mol Aspects Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;27(5-6):426-43. Epub 2006 Sep 26.
95 : Branched-chain amino acids and arginine suppress MaFbx/atrogin-1 mRNA expression via mTOR pathway in C2C12 cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1780(10):1115-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Jun 18.
96 : Influence of branched-chain amino acid supplementation on urinary protein metabolite concentrations after swimming. J Am Coll Nutr. 2006 Jun;25(3):188-94.
97 : Effects of carbohydrates-BCAAs-caffeine ingestion on performance and neuromuscular function during a 2-h treadmill run: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over placebo-controlled study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011 Dec 7;8:22. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-22.
98 : Effect of BCAA intake during endurance exercises on fatigue substances, muscle damage substances, and energy metabolism substances. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2013 Dec;17(4):169-80. doi: 10.5717/jenb.2013.17.4.169. Epub 2013 Nov 28.
99 : Branched-chain amino acids supplementation enhances exercise capacity and lipid oxidation during endurance exercise after muscle glycogen depletion. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011 Mar;51(1):82-8.
100 : Higher branched-chain amino acid intake is associated with a lower prevalence of being overweight or obese in middle-aged East Asian and Western adults. J Nutr. 2011 Feb;141(2):249-54. doi: 10.3945/jn. 110.128520. Epub 2010 Dec 15.
101 : Combined effects of caloric restriction and branched-chain amino acid supplementation on body composition and exercise performance in elite wrestlers. Int J Sports Med. 1997 Jan;18(1):47-55.
102 : Increasing Dietary Leucine Intake Reduces Diet-Induced Obesity and Improves Glucose and Cholesterol Metabolism in Mice via
103 : Leucine in food mediates some of the postprandial rise in plasma leptin concentrations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Sep;291(3):E621-30. Epub 2006 Apr 25.
104 : Leucine supplementation improves leptin sensitivity in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Nutr Res. 2015 Jun 25;59:27373. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v59.27373. eCollection 2015.
105 : Branched-chain amino acid ingestion can ameliorate soreness from eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 May;42(5):962-70. doi: 10.1249/MSS.Ob013e3181c1b798.
106 : Branched-chain amino acid supplementation before squat exercise and delayed-onset muscle soreness. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2010 Jun;20(3):236-44.
107 : Exercise-induced muscle damage is reduced in resistance-trained males by branched chain amino acids: a randomized, double-blind,
108 : Post-exercise carbohydrate plus whey protein hydrolysates supplementation increases skeletal muscle glycogen level in rats. Amino Acids. 2010 Apr;38(4):1109-15. 10.1007/s00726-009-0321-0. Epub 2009 Jul 11.
doi:
109 : Branched-chain amino acid-containing dipeptides, identified from whey protein hydrolysates, stimulate glucose uptake rate in L6 myotubes and isolated skeletal muscles. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2009 Feb;55(1):81-6.
110 : Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. 1971. Obes Res. 1997 Jul;5(4):377-80.
111 : Serotonin spillover onto the axon initial segment of motoneurons induces central fatigue by inhibiting action potential initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2013 Mar 19;110(12):4774-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216150110. Epub 2013 Mar 4.
112 : A role for branched-chain amino acids in reducing central fatigue. J Nutr. 2006 Feb;136(2):544S-547S.
113: Branched-chain amino acids, arginine, citrulline alleviate central fatigue after 3 simulated matches in taekwondo athletes: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016 Jul 13;13:28. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0140-0. eCollection 2016.
114 : Branched-chain amino acids and arginine improve performance in two consecutive days of simulated handball games in male and female athletes: a randomized trial. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 24;10(3):e0121866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121866. eCollection 2015.
[ アスリートのための最新栄養学(上) ]