BCAAとEAAの使い分けは
掲載日:2019.02.14

BCAAに比べ、EAA(必須アミノ酸)のサプリメントはそれほど浸透していないようです。BCAAとEAAを比較する前に、まずはBCAAとホエイについて比較してみましょう。
ホエイプロテインには多くのBCAAが含まれるため、ホエイを飲んでいればBCAAは必要ないという考え方があります。実際のところ、ホエイプロテインを100g飲めば20g以上のBCAAが摂取可能となります。
ただし前述の通り、BCAAを単体で摂取することによる急峻な血中BCAA濃度の増加は、ホエイプロテインでは得られません。
では少なめの量のホエイとBCAAを比較してみましょう。14gのBCAAを摂取させた群と28gのホエイを摂取させた群、28gの炭水化物を摂取させた群に分けて8週間のウェイトトレーニングを行わせました。
その結果、
・体重増加:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・除脂肪体重:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・体脂肪の低下:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・筋力の向上:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
と、すべてにおいてBCAA群がホエイ群を上回りました。(※122)
28gのホエイですと、それに含まれるBCAAは7~8g程度です。
ホエイプロテインには多くのBCAAが含まれるため、ホエイを飲んでいればBCAAは必要ないという考え方があります。実際のところ、ホエイプロテインを100g飲めば20g以上のBCAAが摂取可能となります。
ただし前述の通り、BCAAを単体で摂取することによる急峻な血中BCAA濃度の増加は、ホエイプロテインでは得られません。
では少なめの量のホエイとBCAAを比較してみましょう。14gのBCAAを摂取させた群と28gのホエイを摂取させた群、28gの炭水化物を摂取させた群に分けて8週間のウェイトトレーニングを行わせました。
その結果、
・体重増加:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・除脂肪体重:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・体脂肪の低下:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
・筋力の向上:BCAA群 > ホエイ群 > 炭水化物群
と、すべてにおいてBCAA群がホエイ群を上回りました。(※122)
28gのホエイですと、それに含まれるBCAAは7~8g程度です。
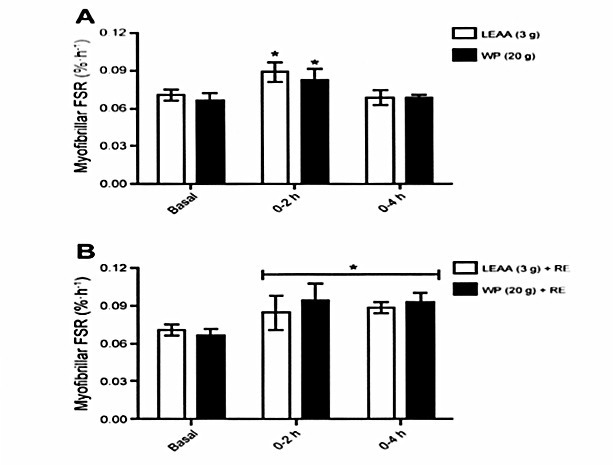
ではホエイにロイシンを追加配合したらどうでしょうか。16.6gのホエイに3.4gのロイシンを追加したところ、普通のホエイを摂取するのと大差ないという結果が出ているようです。(※125)これらの結果から考えると、ホエイ単独よりもBCAA単独のほうがアナボリック効果としては確かに上回るようです。
では血中濃度の上昇速度がBCAAと同等であるEAAの効果はどうでしょうか。
まず15gのEAAと15gのホエイプロテインのタンパク合成効果を比較した研究があります。その結果、EAAのほうが遥かに高い合成効果を示しています。(※126)
しかしEAAの量が少ないとダメかもしれません。
7gのEAAを使った研究では、筋タンパク合成効果はそれほど認められていません。(※127)※125の報告ではロイシンが多ければ少量でも良いとされていますが、追加試験が待たれるところです。
確実なところで、若者でも高齢者でも、EAAを15g摂取しておけば十分なようです。(※128)
この場合、ロイシンの配合量を増やす必要はなく、15gのEAAに含まれるロイシンは絶対量として既に十分だとされています。この研究ではロイシンは2.79g、イソロイシンは1.56g、バリンは1.73gとなっています。
15gのEAAであれば、ホエイと比較して明らかに有利ですが、ではBCAAと比較した場合はどうでしょうか。ロイシン単体とBCAA、EAAをそれぞれトレーニング中に摂取した研究があります。(※129)その結果、タンパク合成酵素であるp70s6kの活性はEAAが一番高くなり、ついでBCAA、最後にロイシン単体という結果でした。
この結果から考えると、十分な量のEAA(15g以上)を摂取すれば、BCAAを上回る効果が期待できそうです。
122 : Consuming a supplement containing branched-chain amino acids during a resistance-training program increases lean mass, muscle strength and fat loss J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009; 6(Suppl 1): P1.
123 : Dose-dependent increases in p70S6K phosphorylation and intramuscular branched-chain amino acids in older men following resistance exercise and protein intake. Physiol Rep. 2014 Aug 7;2(8). pii: e12112. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12112. Print 2014 Aug 1.
124 : Intake of low-dose leucine-rich essential amino acids stimulates muscle anabolism equivalently to bolus whey protein in older women at rest and after exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):E1056-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00481.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 31.
125 : Stimulation of muscle anabolism by resistance exercise and ingestion of leucine plus protein. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Apr;34(2):151-61. doi: 10.1139/H09-006.
126 : Differential stimulation of muscle protein synthesis in elderly humans following isocaloric ingestion of amino acids or whey protein. Exp Gerontol. 2006 Feb;41(2):215-9. Epub 2005 Nov 23
127 : Aging is associated with diminished accretion of muscle proteins after the ingestion of a small bolus of essential amino acids 2005 American Society for Clinical Nutrition
128 : Amino acid ingestion improves muscle protein synthesis in the young and elderly American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism Published 1 March 2004Vol. 286no. 3, E321-E328DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00368.2003
129 : Activation of mTORC1 by leucine is potentiated by branched-chain amino acids and even more so by essential amino acids following resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):C874-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00374.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 6.
では血中濃度の上昇速度がBCAAと同等であるEAAの効果はどうでしょうか。
まず15gのEAAと15gのホエイプロテインのタンパク合成効果を比較した研究があります。その結果、EAAのほうが遥かに高い合成効果を示しています。(※126)
しかしEAAの量が少ないとダメかもしれません。
7gのEAAを使った研究では、筋タンパク合成効果はそれほど認められていません。(※127)※125の報告ではロイシンが多ければ少量でも良いとされていますが、追加試験が待たれるところです。
確実なところで、若者でも高齢者でも、EAAを15g摂取しておけば十分なようです。(※128)
この場合、ロイシンの配合量を増やす必要はなく、15gのEAAに含まれるロイシンは絶対量として既に十分だとされています。この研究ではロイシンは2.79g、イソロイシンは1.56g、バリンは1.73gとなっています。
15gのEAAであれば、ホエイと比較して明らかに有利ですが、ではBCAAと比較した場合はどうでしょうか。ロイシン単体とBCAA、EAAをそれぞれトレーニング中に摂取した研究があります。(※129)その結果、タンパク合成酵素であるp70s6kの活性はEAAが一番高くなり、ついでBCAA、最後にロイシン単体という結果でした。
この結果から考えると、十分な量のEAA(15g以上)を摂取すれば、BCAAを上回る効果が期待できそうです。
122 : Consuming a supplement containing branched-chain amino acids during a resistance-training program increases lean mass, muscle strength and fat loss J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009; 6(Suppl 1): P1.
123 : Dose-dependent increases in p70S6K phosphorylation and intramuscular branched-chain amino acids in older men following resistance exercise and protein intake. Physiol Rep. 2014 Aug 7;2(8). pii: e12112. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12112. Print 2014 Aug 1.
124 : Intake of low-dose leucine-rich essential amino acids stimulates muscle anabolism equivalently to bolus whey protein in older women at rest and after exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):E1056-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00481.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 31.
125 : Stimulation of muscle anabolism by resistance exercise and ingestion of leucine plus protein. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Apr;34(2):151-61. doi: 10.1139/H09-006.
126 : Differential stimulation of muscle protein synthesis in elderly humans following isocaloric ingestion of amino acids or whey protein. Exp Gerontol. 2006 Feb;41(2):215-9. Epub 2005 Nov 23
127 : Aging is associated with diminished accretion of muscle proteins after the ingestion of a small bolus of essential amino acids 2005 American Society for Clinical Nutrition
128 : Amino acid ingestion improves muscle protein synthesis in the young and elderly American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism Published 1 March 2004Vol. 286no. 3, E321-E328DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00368.2003
129 : Activation of mTORC1 by leucine is potentiated by branched-chain amino acids and even more so by essential amino acids following resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):C874-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00374.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 6.
[ アスリートのための最新栄養学(上) ]